Agricultural Density: Understanding How People and Farming Shape the Land
Agricultural density is one of those geography ideas that sounds technical at first, but once you get into it, it tells a powerful story about people, food, land, and the future of our planet. In simple terms, agricultural density helps us understand how many farmers are working the land and how efficiently that land is being used. It connects farming practices with population patterns, economic development, and food security.
At the start of this article, it’s important to say this clearly: agricultural density is not just about numbers. It’s about people’s lives, their livelihoods, and how societies feed themselves. From small family farms to large commercial operations, agricultural density gives us clues about how farming systems work around the world.
In this detailed guide, you’ll learn what agricultural density means, why it matters, how it’s calculated, and how it affects countries at different stages of development. The tone is formal but friendly, the language is clear, and the goal is simple to help you truly understand agricultural density and why it deserves attention.
What Is Agricultural Density?
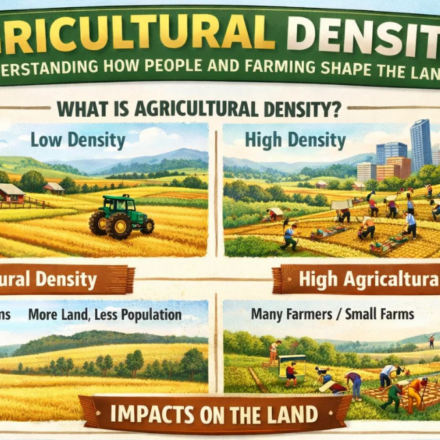
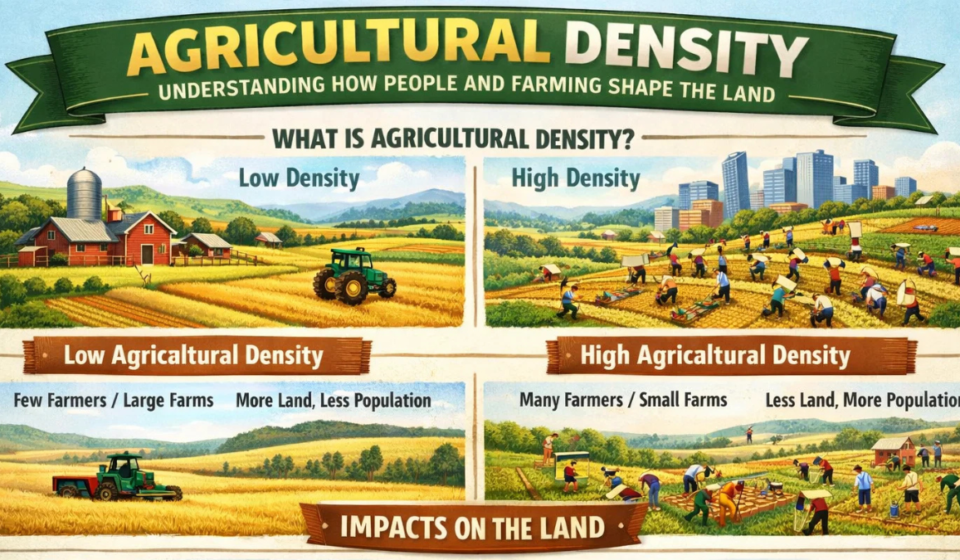
Agricultural density refers to the number of farmers per unit area of arable land. Arable land is land that can be used for farming, especially for growing crops. In other words, agricultural density shows how crowded or spread out farmers are on usable farmland.
To put it plainly:
- A high agricultural density means many farmers are working on a small amount of farmland.
- A low agricultural density means fewer farmers are working on a larger amount of farmland.
This concept is widely used in geography, economics, and environmental studies because it gives insight into farming efficiency, technology use, and economic conditions.
Why Agricultural Density Matters in Geography
Agricultural density matters because it helps geographers and planners understand how land and labor are being used. It’s not just about farming; it’s about development, sustainability, and quality of life.
Here’s why agricultural density is important:
- It shows how dependent a population is on farming.
- It helps explain differences between developed and developing countries.
- It highlights pressure on land and natural resources.
- It supports planning for food production and rural development.
In short, agricultural density acts like a window into a country’s farming system and economic health.
Agricultural Density vs Other Types of Density
To fully understand agricultural density, it helps to compare it with other population measures. Many people mix these terms up, so let’s clear the air.
| Type of Density | Definition | What It Tells Us |
|---|---|---|
| Arithmetic Density | Total population ÷ total land area | How crowded a country is overall |
| Physiological Density | Total population ÷ arable land | Pressure of people on farmland |
| Agricultural Density | Farmers ÷ arable land | Pressure of farmers on farmland |
Unlike arithmetic density, agricultural density focuses only on farmers and farmland. That makes it especially useful for studying rural areas and food systems.
How Agricultural Density Is Calculated
Calculating agricultural density is straightforward, and that’s part of its strength. The formula looks like this:
Agricultural Density = Number of Farmers ÷ Amount of Arable Land
Let’s look at a simple example:
- Country A has 1,000 farmers and 100 square kilometers of arable land.
- Agricultural density = 1,000 ÷ 100 = 10 farmers per square kilometer.
This number helps researchers understand how intensively land is being farmed and whether farmers have enough space and resources.
Agricultural Density in Developing Countries
In many developing countries, agricultural density tends to be high. That’s because a large portion of the population depends on farming, and there may be limited arable land available.
Common features include:
- Small farms worked by families
- Limited access to modern technology
- Heavy reliance on human labor
- Farming mainly for survival rather than profit
In these regions, high agricultural density can lead to land exhaustion and low productivity. Farmers may struggle, not because they lack effort, but because the land is under pressure.
Agricultural Density in Developed Countries
In developed countries, agricultural density is usually low. Fewer people work in farming, but they produce large amounts of food using advanced tools and technology.
Typical characteristics include:
- Large-scale commercial farms
- Advanced machinery and irrigation systems
- Use of fertilizers and improved seeds
- Farming as a business, not just a lifestyle
Here, low agricultural density often means higher efficiency. One farmer can manage large areas of land and feed many people.
The Role of Technology in Agricultural Density
Technology plays a huge role in shaping agricultural density. When technology improves, fewer farmers are needed to produce the same or even more food.
Key technologies that affect agricultural density include:
- Tractors and harvesters
- Irrigation systems
- Genetically improved crops
- Data-driven farming tools
Thanks to these innovations, countries can lower their agricultural density while increasing food production. That’s a win-win situation.
Agricultural Density and Food Security
Food security means having reliable access to enough nutritious food. Agricultural density directly affects food security, especially in rural areas.
High agricultural density can:
- Increase pressure on farmland
- Reduce crop yields
- Lead to food shortages if land degrades
Low agricultural density, when supported by technology, can:
- Increase food output
- Improve food distribution
- Support growing populations
So, agricultural density isn’t just a statistic it’s a key factor in feeding the world.
Environmental Impacts of Agricultural Density
The environment feels the effects of agricultural density, whether it’s high or low. When too many farmers work the same land, the soil can lose nutrients, forests may be cleared, and water resources can dry up.
Environmental concerns linked to agricultural density include:
- Soil erosion
- Deforestation
- Water pollution
- Loss of biodiversity
Sustainable farming practices can help balance agricultural density and protect the environment at the same time.
Agricultural Density and Economic Development
There’s a strong link between agricultural density and economic development. Countries with high agricultural density often rely heavily on agriculture for income, while those with low agricultural density usually have diversified economies.
As economies grow:
- People move from farming to industry and services
- Agricultural density decreases
- Productivity per farmer increases
This shift doesn’t mean farming becomes less important. Instead, it becomes more efficient and better supported.
Advantages of Understanding Agricultural Density
Knowing about agricultural density offers several benefits, especially for planners and policymakers.
Advantages include:
- Better land-use planning
- Improved food production strategies
- Stronger rural development policies
- Smarter environmental protection
Understanding agricultural density helps leaders make informed decisions that benefit both people and the planet.
Challenges Related to Agricultural Density
Despite its usefulness, agricultural density also highlights challenges that need careful attention.
Some key challenges are:
- Overcrowding on farmland
- Limited access to modern tools
- Climate change impacts
- Unequal land distribution
Addressing these challenges requires cooperation between governments, farmers, and communities.
Agricultural Density and Sustainable Farming
Sustainability is the future of farming, and agricultural density plays a central role in that future. Sustainable farming aims to produce enough food without harming the environment or exhausting resources.
Sustainable practices include:
- Crop rotation
- Organic farming
- Efficient water use
- Soil conservation methods
When agricultural density is managed wisely, sustainability becomes achievable rather than just a buzzword.
Agricultural Density in a Changing World
The world is changing fast. Climate change, population growth, and urbanization are reshaping agricultural density across the globe.
Trends to watch include:
- Migration from rural to urban areas
- Increased use of smart farming technology
- Greater focus on climate-resilient crops
- Policies supporting small farmers
These changes show that agricultural density is not fixed. It evolves with society’s needs and innovations.
Common Misunderstandings About Agricultural Density
Many people misunderstand agricultural density, assuming that high density is always bad or low density is always good. That’s not true.
Important clarifications:
- High agricultural density can support communities if managed well.
- Low agricultural density doesn’t guarantee sustainability.
- Context matters technology, climate, and policy all play roles.
Understanding the full picture helps avoid oversimplified conclusions.
Key Facts About Agricultural Density
Here’s a quick recap in bullet form to lock in the main ideas:
- Agricultural density measures farmers per unit of arable land.
- It differs from arithmetic and physiological density.
- High agricultural density often appears in developing regions.
- Low agricultural density is common in developed countries.
- Technology strongly influences agricultural density.
- It affects food security, the environment, and economic growth.
Final Thoughts on Agricultural Density
As we come to the end, it’s clear that agricultural density is more than a textbook term. It’s a powerful concept that explains how people, land, and food systems interact. From crowded fields in developing regions to vast mechanized farms in developed countries, agricultural density tells a story of adaptation, challenge, and progress.
By understanding agricultural density, we gain insight into food security, environmental sustainability, and economic development. It helps students, researchers, and policymakers see the bigger picture and make smarter choices.
In a world facing climate change and population growth, paying attention to agricultural density isn’t optional it’s essential. With the right balance of technology, policy, and care for the land, agricultural density can support a healthier, more food-secure future for everyone.
You may also read
Small Gear Pumps: A Complete and Trusted Guide for Beginners and Professionals